We reach more than 65,000 registered users in Dec!! Register Now

Newly dated 85-million-year-old dino eggs could improve understanding of Cretaceous climate
- September 15, 2025
- 613 Views
- 0 Likes
- 0 Comment
Dating dinosaur eggs is difficult: available methods are limited and prone to errors because measurement proxies – such as volcanic rocks or crystals – may have changed between egg laying and dating attempts. Now, in a first for paleontology, researchers used a new method to date dinosaur eggs by firing lasers at eggshell fragments. This way, eggs in central China have been dated to the late Cretaceous, making them about 85 million years old. The findings could tell researchers about dinosaur populations and the climate millions of years ago.
In the Cretaceous period, Earth was plagued by widespread volcanic activity, oceanic oxygen depletion events, and mass extinctions. Fossils from that era remain and continue to give scientists clues as to what the climate may have looked like in different regions.
Now, researchers in China have examined some of them: dinosaur eggs found at the Qinglongshan site in the Yunyang Basin in central China. This is the first time that dinosaur eggs have been dated using carbonate uranium-lead (U-Pb) dating. The team published their results in Frontiers in Earth Science.
“We show that these dinosaur eggs were deposited roughly 85 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period,” said corresponding author Dr Bi Zhao, a researcher at the Hubei Institute of Geosciences. “We provide the first robust chronological constraints for these fossils, resolving long-standing uncertainties about their age.”
New dates
Qinglongshan is China’s first national dinosaur egg fossil reserve. There, more than 3,000 fossilized eggs are spread across three sites. Most fossils are embedded in different stones, such as breccias, breccia and siltstone mixes, and fine sandstones. The eggs have mostly remained in their original location and show only minimal deformation. The majority is thought to belong to a single species, Placoolithus tumiaolingensis, which belongs to the family Dendroolithidae, a group characterized by highly porous eggshells. The sampled calcite-filled dinosaur egg fossil came from a cluster of 28 eggs embedded within breccia-bearing siltstone.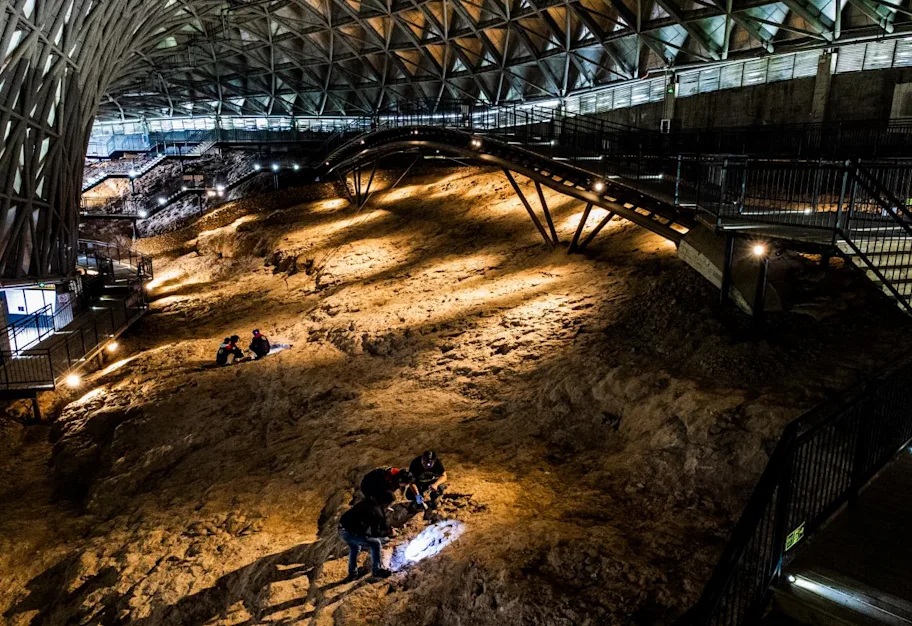
The results showed that the eggs from this cluster were deposited around 85 million years ago, with the possibility of them having been deposited around 1.7 million years earlier or later. Their age means they’ve been laid during the Late Cretaceous, an epoch lasting from approximately 100 to 66 million years ago. They are the first reliably dated fossils from the Qinglongshan site.
List of Referenes
- Qingmin Chen, Xing Cheng, Jian Wang, Bi Zhao, Bi Zhao, Shukang Zhang, Youfeng Ning, Gaohong Wang, Kaikai He, Wenshuo Zhang, Dongxiang Yu, Jiangli Li, Yarui Zou, Gang Chen, Min Li, Hai Cheng. Geological age of the Yunyang dinosaur eggs revealed by in-situ carbonate U-Pb dating and its scientific implications. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10 September 2025 DOI: 10.3389/feart.2025.1638838
Cite This Article as
No tags found for this post