Discussion with Santanu Das on Statistical Isotropy (SI) violation in the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB)
-
April 16, 2022
-
1409 Views
-
0
Likes
-
Comment
SIToolBox, a new software package developed for estimating the isotropy violation in the CMB sky.
Can you please describe the broad field of your research?
Cosmology is the study of a combination of the natural sciences, particularly astronomy and physics, to understand the universe as a whole. In the standard model of cosmology, all the matter and energy were created during an event called Big Bang about 14 billion years ago. Then the universe started expanding and slowly created all the structures within. The universe almost took 371 000 years to cool down. The matter became neutral, and it allowed the light to travel freely through the Universe.
Over the period of time the primeval intensity of radiation has considerably weakened and the energy of the radiation decreased. Today we can detect the light in the microwave and it is known as Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB).
CMB was first theoretically predicted by Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman in 1948. Later, in 1964, US physicist Arno Penzias and radio-astronomer Robert Woodrow Wilson accidentally observed CMB while they were working on Holmdel Horn Antenna. They estimated its temperature to be around 3.5 K. Today the most accurate measurement of CMB places the CMB temperature to 2.726K.
CMB provides astronomers the earliest blueprint of the universe, the closest possible time to the Big Bang detectable through electromagnetic radiation (light). It is currently one of the most promising ways we have for understanding the birth and evolution of our Universe. This makes the research in CMB challenging and equally exciting.
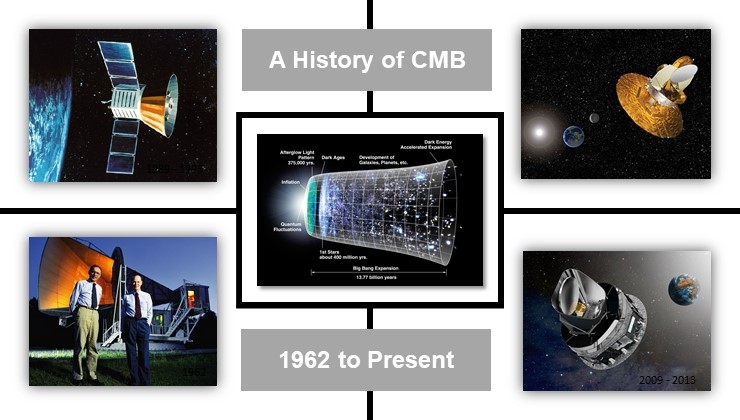
The 15 meter Holmdel horn antenna at Bell Telephone Laboratories in Holmdel, New Jersey is shown in the left bottom. Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson accidentally discovered the cosmic microwave background radiation in 1962 while trying to remove a constant noise background from the signal. They were awarded the 1978 Nobel prize in physics. In the left top, right top and the right bottom shows COBE, WMAP and Planck satellite which are the milestones in the history of CMB observation. In the middle, we have shown the expansion history of the universe - starting from Big Bang to the Present time.
Describe the problem that you are solving?
The modern cosmological models relay on the Copernican principle, which says that the universe is considered as homogeneous and isotropic. Homogeneous means that the universe presents the same properties everywhere on a cosmological scale, whereas isotropy means if you look at the different directions of the universe it will look the same.
Theory predicts that CMB is statistically isotropic (SI), which means the intensity of CMB is statistically the same from all the direction of the sky. The standard model of cosmology relays on this assumption. Therefore, the SI properties of CMB have been under intense scrutiny. NASA's WMAP-7 mission detected some SI violations in CMB. However, later it was found to be an instrumental artifact.
Even if the intrinsic CMB is SI, there can be various sources of SI violations in measured CMB. Firstly, we are measuring CMB from our solar system in our galaxy, which has a velocity with respect to the CMB rest frame. Therefore, the Doppler boost of the CMB will introduce SI violation. Different observational artifacts like scan patterns of the CMB experiments; asymmetric beam patterns due to unavoidable side lobes; masking of point sources, galactic plane, a bright region like LMC, SMC; anisotropic noise patterns of the detector, may introduce the isotropy violation in CMB. SI violations in the CMB sky may also arise due to non-standard theoretical models. Whatever be the source of SI violation, its important to develop a proper data analysis technique that can measure the SI violation in CMB.
We are working on developing of a software package, names as SIToolBox that can calculate the isotropy violation in the CMB sky. This is the first-ever such a software package developed for CMB data analysis.
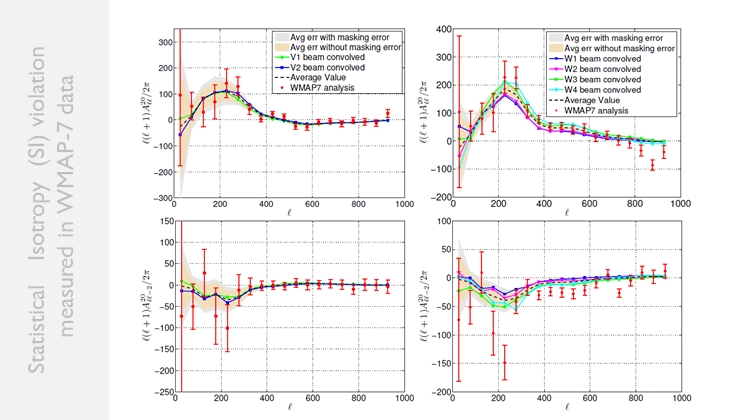
The graphs show statistical isotropy (SI) violation signals discovered by different instruments in WMAP-7 year data. If there were no SI violation then all the points would have been zero. Later it was found that the signal that was detected actually came from some observational artifact.
What are the new results from your research?
Presently there are multiple methods for measuring the SI violation in the CMB sky. One of the highly recognized techniques is the Bipolar Spherical Harminics (BipoSH) method proposed by Hajian, Souradeep in a 2003 Astrophysical Journal (ApJ) paper. Since then several developments have been done in the BipoSH formalism.
In this particular research, we develop the CMB SI violation measurement package, known as SIToolBox, which can estimate the isotropy violation in CMB sky using BipoSH formalism. Previous SI violation detection algorithms used bias subtraction methods while accounting for the masking and anisotropic noise, etc. However, those may lead to errors. SIToolBox, uses a completely Baysian technique to measure the SI violation in CMB sky, which is very accurate than the previous techniques.
We use SIToolBox for measuring the isotropy violation on different simulated data set where a very small amount of SI violation signal has been injected in the presence of high instrumental noise and masking. Our algorithm can very accurately estimate the injected signal. This shows the efficacy of the algorithm.
SIToolBox also contains modules to predict the dipole modulation and the Doppler boost signal from the CMB sky. The package has been made public through github.
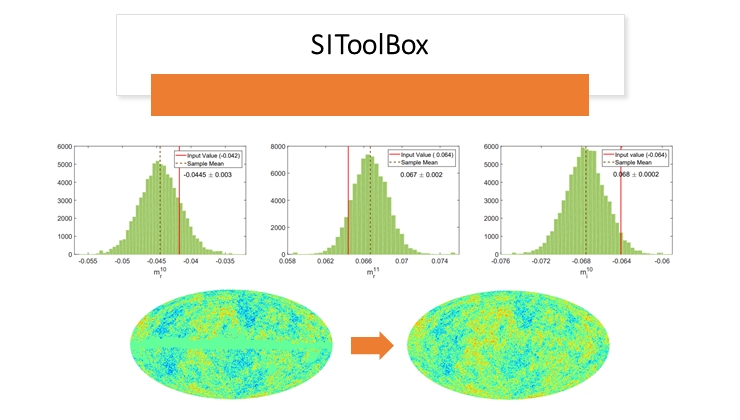
An application of SIToolBox for Dipole modulation estimation. The red solid line shows the injected signals and the dotted lines show that recovered signal from the noisy skymap. In the bottom, we have shown the input map to SIToolBox. Some of the parts are masked there. In the output, we can also recover the masked parts of the input maps.
Say something about your team who were involved in developing SIToolox?
The package has been developed by myself, Santanu Das. The project was started while I was in a Ph.D. The initial algorithm of the project was proposed by prof. Benjamin Wandelt at IAP and coordinated by prof Tarun Souradeep. We work on the algorithm and the first article on this research was published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics (JCAP) in 2015.
After Ph.D., I joined in a joint position of the University of Wisconsin, Madison and Fermilab as a postdoctoral researcher for Tianlai project. While in postdoc I also worked on CMB SI violation and developed the algorithm further. The code is restricted and rewritten to create SIToolBox. The work is published in Monthly Notice of Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS). This is the first software developed for measuring the isotropy violation of the CMB sky using a completely Bayesian technique.
The software package is written in Fortran 90. Initially, the parallelization was done using a distributed architecture in Mpi. However, later it was replaced using an OpenMP architecture. The package contains different standalone codes and callable subroutines which can be run directly or used by software developers as a function in their codes.
What is your future goal?
Presently SIToolBox can only be used for testing the isotropy violation in CMB temperature on simulated maps. Measuring the SI violation from the real cosmological data using SIToolBox is an interesting and important future project.
However, recently we also got the CMB polarization maps. SIToolBox package can be used for testing the SI violation in CMB polarization, and many other fields of astronomy. In most of the cases, we either need a very little or no modification in the present version of SIToolBox.
Different intensity mapping surveys, like Tianlai, HIRAX, FAST, GBT, etc. are either mapping or planning to map the 21 cm sky signal. Therefore, SIToolBox can be used directly to analyze the intensity mapping data in the future, which will help astronomers to understand the true shape of the universe.

Different upcoming CMB and HI intensity mapping experiments, where SIToolBox can be used for testing the SI violation in the universe.
List of References
Cite this Page as
Keywords
CMB
Statistical Isotropy Violation
SIToolBox
Cosmology
Astrophysics
Data Analysis
Cosmological software
















